Synology DiskStation DS1821+ NAS Review
Testing Methodology
| System Configuration | ||
| Component | Product Name | Provided By |
| Case | Open Test Bench | |
| CPU | Intel Core i7 9700K | |
| CPU Cooler | Alphacool Eisbaer Aurora 240 CPU – Digital RGB | Alphacool |
| Motherboard | EVGA Z390 FTW | EVGA |
| Ram | (2) 8GB Corsair DDR4-3200 CMW16GX4M2C3200C16 | Corsair |
| GPU | MSI GeForce RTX™ 2080 Super GAMING X TRIO | MSI |
| Monitor | BenQ EL2870U 28 inch 4K HDR Gaming Monitor 3840×2160 @ 60 Hz | |
| Hard Drives | Adata XPG SX8200 PRO (512GB) | Adata |
| Power Supply | Thermal Take Tough Power RGB 80 Plus Gold 750W | |
| Network Switch | MicroTik CRS317-1G-16S+RM |
|
| Network Cards | Synology E10G21-F2 , Dell RT8N1 Mellanox |
Synology |
| Drivers | (4) Synology HAT5300-8T , (2) SK hynix Gold P31 M.2 NVMe 500Gb |
Synology |
| Transceivers | 10Gtek 10Gbase-SR SFP+ |
|
4 Synology HAT5300-8T 8 TB 7200 RPM NAS drives were installed and used in the NAS tests.
For cache benchmarks, I will be using 2SK Hynix Gold P31 PCIe NVMe Gen3
M.2 2280 Internal SSD – 500GB NVMe drives.
A single port DELL RT8N1 SFP+ network card
with 10Gtek SFP+ transceiver was installed in the test system.
The Synology DS1821+ in all RAID arrays used a Single Static Volume.
Network Layout
For all tests, the NAS was configured to use the a single network interface.
One Fiber Patch Cable was connected to the MicroTik CRS317-1G-16S+RM switch to
NAS and one Fiber Patch Cable cable was connected to the workstation from the
switch. Testing was done on the PC with only 1 network card active; other
network cards and the corresponding software were disabled for the testing.
The switch was cleared of any configuration and left in a un-configured state.
Jumbo frames were set to 9000 MTU on NAS, Switch and Client PC.
Software
All testing is done based on a single client accessing the NAS.
To test NAS Performance I used The Intel NAS Performance toolkit.
The Intel NAS Performance toolkit simulates various tasks for storage devices such as video streaming, copying files and folders to and from the NAS as well as creating content directly
on the NAS. To limit caching, a Ram Drive was used to limit the memory module to 2
GB in all tests. All options in the Performance toolkit were left that the defaults. The NAS performance test is free to download. You can pick up a copy for yourself here.
In addition to Intel NAS Performance toolkit I have run ATTO Disk Benchmark tool to get better throughput metrics on the performance of the Synology DiskStation DS1821+
All tests were run a total of three times then averaged to get the final result.
RAID 0,1,5 were tested.
Tests were run after all the RAID arrays were fully synchronized
RAID Information
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Images courtesy of Wikipedia | ||
JOBD or Just a Bunch Of Disks is exactly what the name describes. The hard drives have no actual raid functionality and are spanned at random data is written at random.
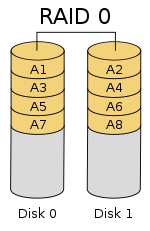
RAID 0 is a stripe set and data is written across the disks evenly. The advantage of RAID 0 is speed and increased capacity. With RAID 0 there is no redundancy and data loss is very possible.
RAID 1 is a mirrored set and data is mirrored from one drive to another. The advantage of RAID 1 is data redundancy as each piece of data is written to both disks. The disadvantage of RAID 1 is write speed is decreased as compared to RAID 0 due to the write operation is performed on both disks. RAID 1 capacity is that of the smallest disk.
RAID 10 combines the 1st two raid levels and is a mirror of a stripe set. This allows for better speed of a RAID 0 array but the data integrity of a RAID 1 array.
RAID 5 is a stripe set with parity. RAID 5 requires at least 3 disks. Data is striped across each disk, and each disk has a parity block. RAID 5 allows the loss of one drive without losing data. The advantage to RAID 5 is read speeds increase as the number of drives increase but the disadvantage is write speeds are slower as the number of drives is increased. There is overhead with RAID 5 as the parity bit needs to be calculated and with software RAID 5 there is more of a performance hit.
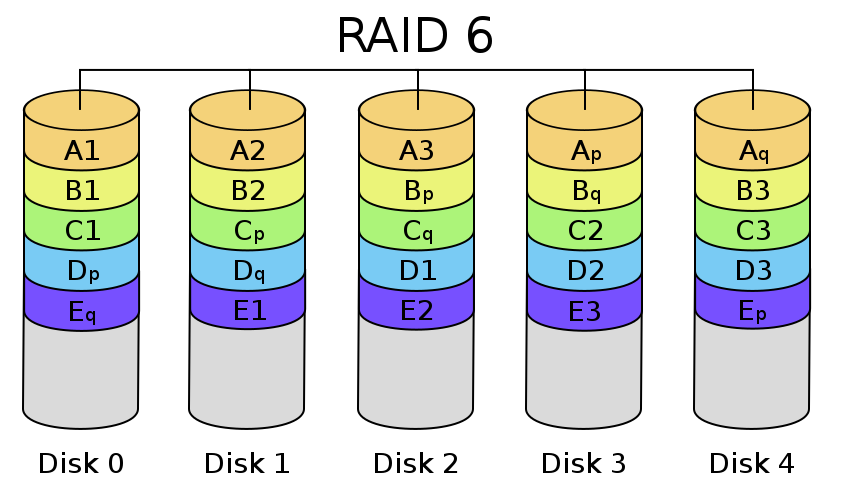
RAID 6 expands on RAID 5 by adding an additional parity block to the array that is distributed across all the disks. Since there are two parity blocks in the array more overhead is used with a RAID 6 array.
For a full breakdown of RAID levels, take a look at the Wikipedia article here.
RAID configurations are a highly debated topic. RAID has been around for a very long time. Hard drives have changed, but the technology behind RAID really hasn’t. So what may have been considered ideal a few years ago may not be ideal today. If you are solely relying on multiple hard drives as a safety measure to prevent data loss, you are in for a disaster. Ideally you will use a mutli-drive array for an increase in speed and lower access times and have a backup of your data elsewhere. I have seen arrays with hot spares that had multiple drives fail and the data was gone.








