CRYORIG C7 CPU Cooler Review: On the Topic of Clearance
A Closer Look at the CRYORIG C7
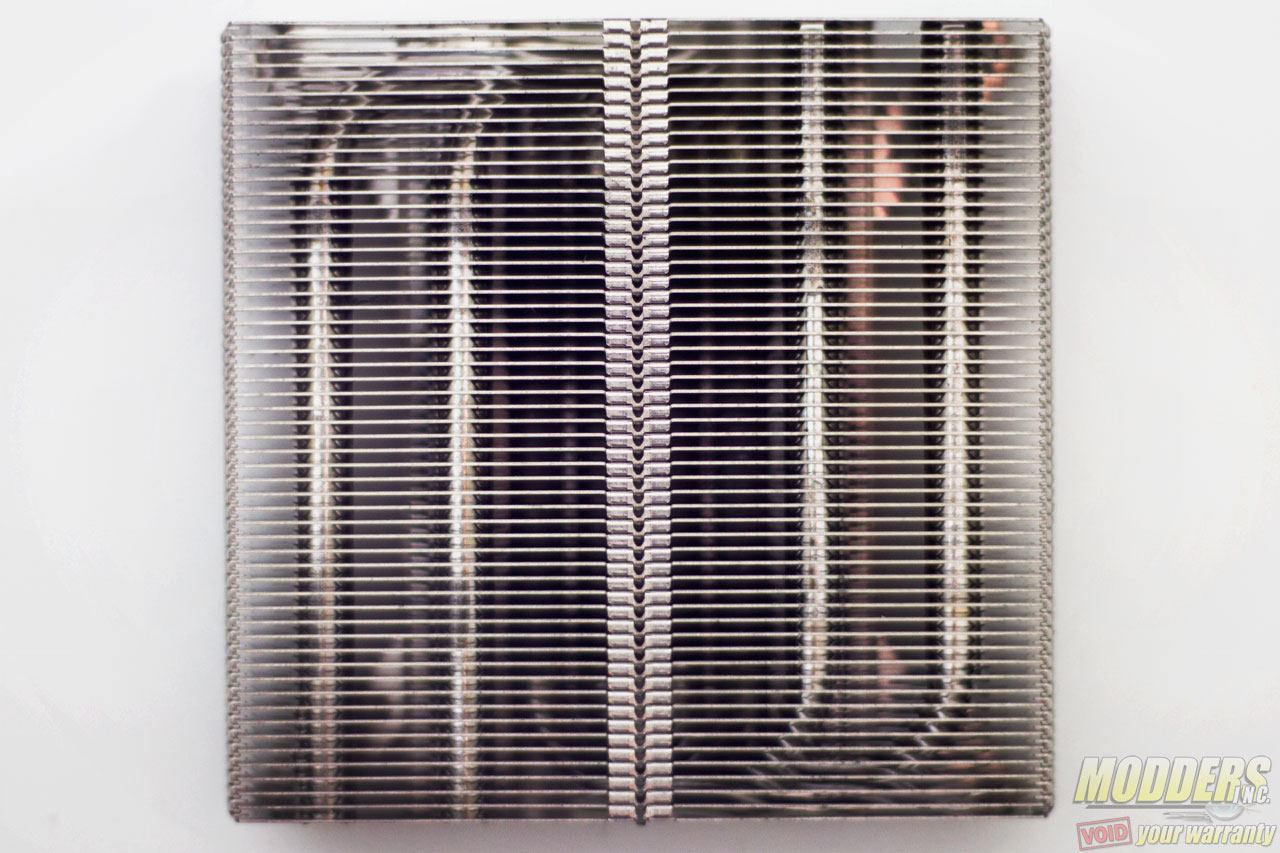
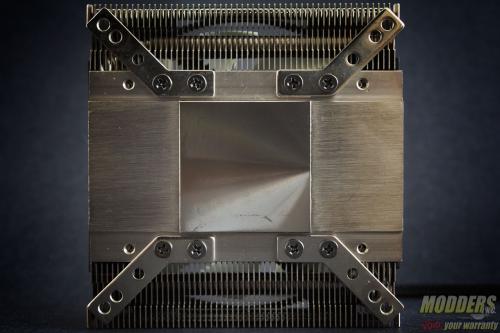
The CRYORIG C7 has four 6mm heatpipes arranged alternately in pairs and stems moderately upward, curving toward each other but not protruding past the aluminum fin set. Heat from the contact surface travels from these heatpipes and are distributed to the 51-piece aluminum fin array which rises up to 32mm from the base.
The sides of the CRYORIG C7 have an open-style fin arrangement except for the folded spine row on the side. The CRYORIG C7 conforms with a 95 x 95mm square layout within the Intel LGA115x keep-out zone but there are notches from where the built-in 92mm fan latches on to plus the plastic assembly which extend it to 97 x 97 mm square at the top.
Out of the box, the stand-offs come pre-attached for LGA115x systems but this can easily be unscrewed and moved to different slot if installing on an AMD or different socket.
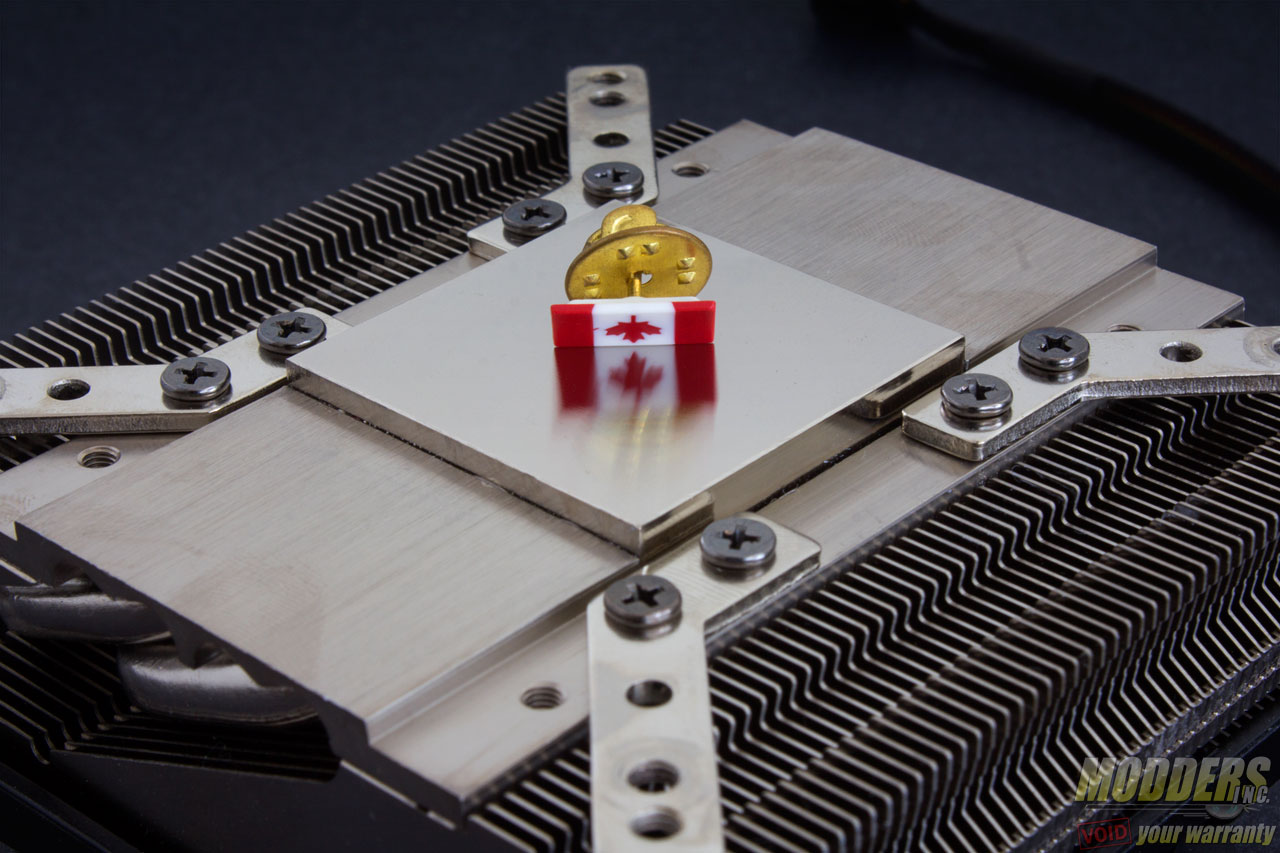
The nickel plated copper contact surface measures 37.95 x 37.95 mm and has rounded visible fine machined marks that are not centered. This contact surface protrudes slightly from the rest of the base.
To minimize noise from vibration of the 2500RPM 92mm fan, there are rubberized pads on four corners although the latching part of the fan mount is part of the plastic housing and not padded. This fan hugs on tightly to the heatsink body and does not come off easily hence the padding is on the corners not on the actual latch.
The fan bundled is a slim 92mm fan that measures 15mm tall compared to standard fans which are 25mm thick . It has 11 white blades that has a steeper upward curve as it moves toward the hub. The hub measures 33mm while the distance from the hub to the frame is 29.5mm. The intake side of the frame has acceleration channels that help feed air into the blades and are semi-segmented to draw air from the sides as well. Functionally, the backside of these acceleration channels also serve as cable management routing channels for the sleeved fan cable.
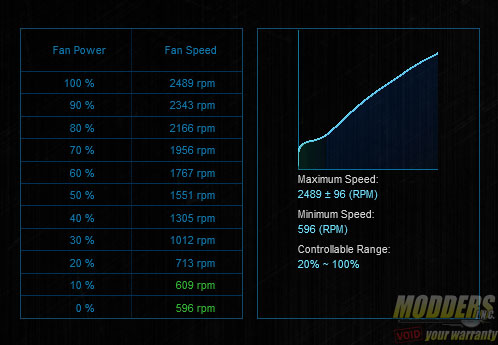
Readings from ASUS Fan Xpert II confirm the real-world controllable PWM range: